Published
by Rogers Corporation
Corporate
Picture a high-speed train packed with passengers during rush hour.
Suddenly, an electrical fault sparks a small fire.
Without the right fire-resistant materials, the fire could spread quickly, releasing toxic smoke and endangering the lives on board.
However, with materials designed to meet stringent rail industry fire safety specifications, the fire can be contained, enabling safe evacuation and saving lives.
This scenario showcases the mission-critical role of selecting reliable, compliant materials for rail applications. At Rogers Corporation, we don't just meet these rigorous demands — we exceed them. Our materials promote safety and enhance the reliability and comfort of rail transportation systems worldwide.
In this blog, we will explore critical rail industry specifications, such as EN 45545-2 and NFPA 130, and highlight how Rogers innovative materials surpass these standards. Additionally, we will explore the key applications of our high-performance materials in the rail industry.
What Are EN 45545-2 and 49CFR238/NFPA 130 Rail Fire Safety Standards?
Rogers Corporation engineered materials are specifically designed to meet and exceed global rail safety standards, including 49CFR238/NFPA 130 and EN 45545-2. Exceeding these standards means that materials not only meet current regulatory requirements, but also offer enhanced performance under extreme conditions, and a higher level of safety. This contributes to the long-term reliability and operational efficiency of rail systems.
EN 45545-2: European Rail Fire Safety Standard
EN 45545-2 is the mandatory European standard for materials used in the manufacture of rail vehicles. It aims to protect passengers and staff from fire on board railway vehicles. It specifies the testing methods and performance criteria for fire risk levels and materials groups.
The primary goal is to minimize the risk of fire and ensure passenger safety by setting stringent criteria for:
- Flame spread
- Heat release rates
- Smoke density
- Toxic gasses when ignited
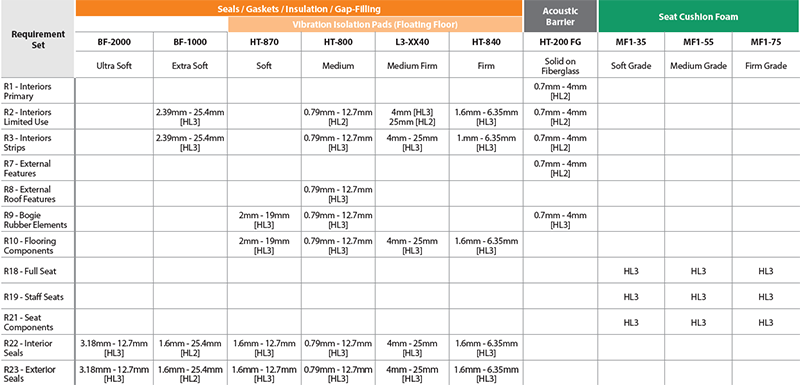
The standard assigns a hazard level depending on the railcar's intended use and further classifies applications and requirements. The material requirement set (R1, R2...) is dependent on the train car type (HL rating) and product classification (IN1A, EC2). See the image below for more details.
| Hazard Level Classification HL1, HL2, HL3 |
Product Classification IN1A, EX2, F1… |
Requirement Set R1, R2, R3… |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Which Rogers Materials Are EN 45545-2 Compliant?
Our materials are rigorously tested to meet and exceed these classifications, providing robust fire safety solutions across the rail sector.
Rogers materials that meet EN 45545-2 include BISCO® HT-800, BISCO® HT-200 and BISCO® HT-6360.
49CFR238/ NFPA 130: North American Fire Safety Standards
49CFR238/NFPA 130 is the North American standard for flame, smoke and toxicity (FST). The standard specifies fire protection and life safety requirements for underground, surface, and elevated fixed guideway transit and passenger rail systems. Key aspects of NFPA 130 include:
- Fire resistance of materials
- Smoke management
- Emergency egress
- Vibration and noise control
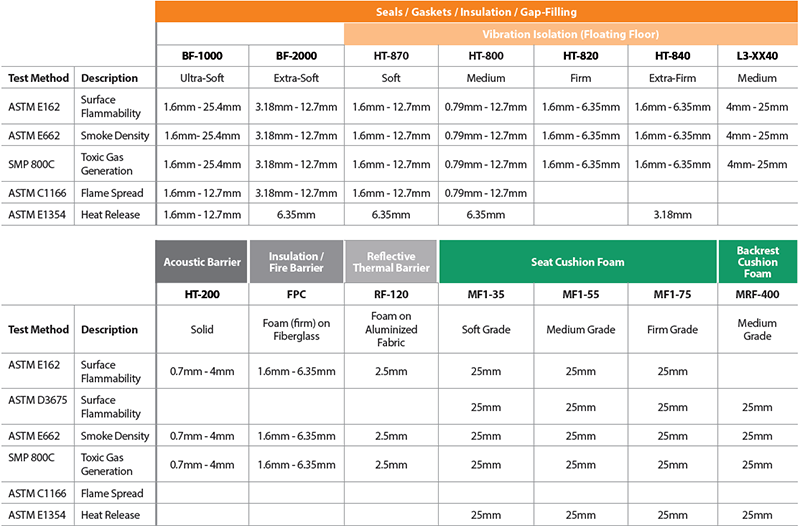
Key tests involved in NFPA 130 compliance include:
| ASTM E162 Surface Flammability | This test method measures and compares the surface flammability of materials when exposed to a prescribed level of radiant heat energy. It is intended for use in measurements of the surface flammability of materials exposed to fire. |
| ASTM E662 Smoke Density | This test method provides a means for determining the specific optical density of the smoke generated by the specimens of materials and assemblies under specified exposure conditions. |
| SMP 800-C Toxic Gas Generation | The Bombardier SMP 800-C measures the toxic gas generation from the combustion of materials used in the rail car construction. |
| ASTM C1166 Flame Spread | This test method is designed to differentiate the flame propagation characteristics of dense or cellular elastomeric compounds used in gaskets, setting blocks, shims, or spacers. |
| ASTM E1354 Heat Release | This test method is used primarily to determine the heat evolved in, or contributed to, a fire involving products of the test material. Also included is a determination of the effective heat combustion, mass loss rate, the time to sustained flaming, and smoke production. |
| ASTM D3675 Surface Flammability | This test method is intended for use when measuring the surface flammability of flexible cellular materials exposed to fire. |
Which Rogers Materials Meet 49CFR238/ NFPA 130?
Rogers materials that meet 49CFR238/ NFPA 130 are BISCO MF1, HT-800, L3 and HT-200.
Why Fire Safety Standards Matter for Modern Rail Car Design
Meeting fire safety standards like EN 45545-2 and 49CFR238/NFPA 130 is critical for ensuring passenger safety and system reliability in rail cars. These standards help reduce the risks of fire, smoke, and toxic gas emissions in key areas like doors, HVAC systems, and passenger compartments. By complying with these regulations, designers can protect passengers while ensuring long-term performance and safety in rail systems.
Rogers Materials Compliance to Rail Standards
Rogers Corporation materials are engineered with innovation and reliability in mind. Our portfolio of rail materials is designed and tested to meet and exceed the demanding requirements of global rail standards.
We continuously test our materials against flame, smoke, and toxicity requirements to ensure their performance under the harshest conditions. No matter where your project is located, Rogers provides fire-safe solutions that meet EN 45545-2, NFPA 130, and other global rail standards.
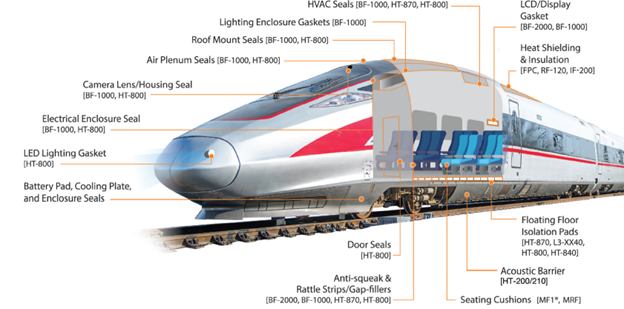
Key Rail Application Areas
Rogers high-performance materials support a wide range of interior and exterior rail applications, enhancing safety, durability, and passenger comfort. Some of our key application areas include:
- HVAC seals
- Roof mount seals
- Door seals
- Electrical/enclosure seals
Noise, Vibration, and Anti-Rattle Management
- Acoustic absorbers/sound barrier
- Floating floor insulation pads
- Anti-squeak and rattle strips
- Gap fillers
Gasketing
Other
BISCO Silicone Material Solutions in Rail Cars
Why Choose Rogers for Rail Safety Solutions?
Selecting the right materials for rail applications is important to promote safety, compliance, and passenger comfort. Rogers Corporation innovative materials are designed to meet the most stringent standards, including EN 45545-2 and NFPA 130, while also delivering reliability, performance, and versatility.
When you choose Rogers, you can be confident that your rail projects can benefit from our decades of expertise, rigorous testing, and commitment to safety.
Learn more about how Rogers materials can benefit your rail applications or contact one of our knowledgeable Sales Engineers.
Let’s work together to promote safety, reliability, and performance.
Related Content
- Winter-Proof Your Train Design with ARLON® Water-Resistant Flexible Heaters
- Top 7 Unique Silicone Advantages You Can't Ignore
- How to Choose the Right Silicone: Top 6 Considerations
Tags:
Rail
Published on Nov 11, 2024